What is a 409A valuation?
A 409A valuation is an independent appraisal of the fair market value (FMV) of a private company’s common stock on the date of issuance. A 409A valuation is used to set the strike price for stock options issued to employees. Appraisers try to determine what a company’s shares would sell for in an ideal market where buyers and sellers possess the same information about a company and its finances.
To do so, appraisers consider factors such as a company’s current assets, its cash flows, comparable public companies, and the implied valuation from any recent secondary transactions. A 409A valuation is based on guidance and standards established in section 409A of the IRS’s internal revenue code (IRC).
In order to offer or issue equity to service providers, understanding the fair market value is crucial unless you want to risk severe IRS penalties for the company and equity holders. So if you want to offer equity, an independent 409A valuation can be helpful.
We’ll help you understand the basics of a 409A valuation so you can choose a valuation provider with confidence. To see what one looks like, download a sample 409A valuation report below.
409A valuation vs. post-money valuation
There are two main types of valuations for private companies: a post-money valuation and a 409A valuation. Both help you understand how much a company is worth, but in different ways.
A 409A valuation:
-
Is used to determine the FMV of one share of a company’s common stock
-
Sets the strike price for stock options issued to founders, employees, and advisors
-
Is based on guidelines in the Internal Revenue Code
-
Is typically determined by a third-party 409A valuation provider
-
Protects employees from taxes and IRS fines if done correctly
A post-money valuation:
-
Is determined by the price of preferred shares, which are more valuable than common stock
-
Is based on how much investors paid for their ownership stake during fundraising
Do I need a 409A valuation?
If you offer equity (or plan to), it is best practice to obtain an independent 409A valuation before you can issue your first common stock options. Early-stage companies and founders also need 409A valuations to keep shareholders from paying tax penalties that may otherwise be assessed by the IRS; a reputable 409A valuation provider can help you take advantage of “ safe harbors."
When do I need a 409A valuation?
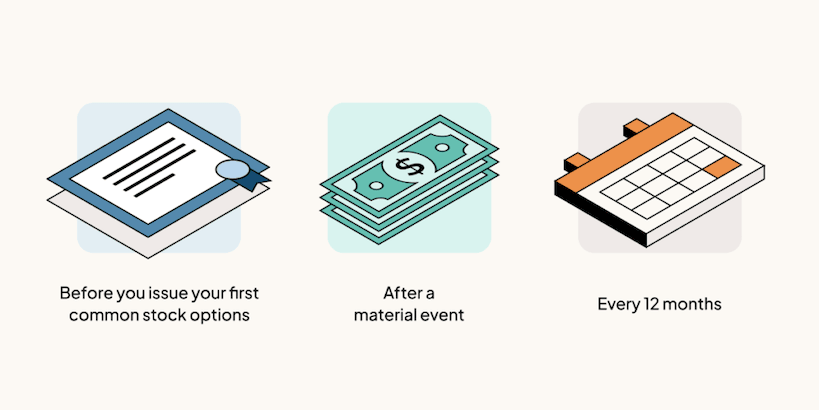
You should get a 409A valuation:
-
Before you issue common stock options to your first hire or advisor. Generally, you should get your company’s first 409A valuation before you issue your first common stock options, which are typically granted to your first hire or advisor.
-
After any material event. Material events are most frequently a financing round, but can also include any significant operational or financial change—including changes in the economy. More on 409A material events below.
-
If you’re approaching an IPO, merger, or acquisition
How long are 409A valuations valid?
409A valuations are valid for a maximum of 12 months after the effective date—or until a material event occurs. A material event is something that could affect a company’s stock price.
For most early-stage startups, a “qualified financing” is the most commonly encountered material event. A qualified financing typically includes a sale of common shares, preferred equity, or convertible debt to independent, institutional investors at a negotiated price.
What is a 409A material event?
Outside of a financing, other events may be considered material:
-
A significant, new, or lost contract that represents a material change in revenue, including annual recurring revenue (ARR).
-
Any material, closed acquisition with your company as the buyer or seller.
-
Your company received a term sheet from a potential acquirer.
-
Strategic partnership that is likely to open new markets or improve margins.
-
Regulatory changes that significantly increase or decrease your addressable market.
If you aren’t sure, reach out to a 409A valuation provider or consult your lawyer.
How much does a 409A valuation cost?
Some providers offer standalone 409A valuations, while others offer bundled services. For standalone valuations, the cost ranges anywhere from $1,000 to over $10,000, depending on the size and complexity of your company.
At Carta, 409A valuations are included in an annual subscription along with cap table management.
Common 409A valuation methodologies
Independent appraisers have an obligation to ensure that your 409A and FMV is “fair.” There are three standard methodologies providers use during a 409A: market approach, income approach, and asset approach.
1. Market approach (OPM backsolve)
When your company raises a financing round, valuation providers typically use the option pricing model (OPM) backsolve method. It can be safely assumed that new investors paid fair market value for the equity, but investors receive preferred stock. So, adjustments must be made to determine the FMV for common stock.
Other market-based approaches use financial information like revenue, net income, and EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) from comparable public companies to estimate the company’s equity value.
2. Income approach
For businesses with sufficient revenue and positive cash flow, valuation providers often use the straightforward income approach. This method defines a company’s value based on its expected future cash flows, adjusted for risk.
3. Asset approach
The asset approach is often used for early-stage companies that haven’t raised money and don’t generate revenue. This methodology calculates a company’s net asset value to determine a proper valuation.
What do I need for a 409A valuation?
Once you’ve selected a 409A appraiser, you need to compile and share some important information about your business. As an example, Carta’s requirements are listed below.
Company details
-
Name of your CEO
-
Name of your external audit firm (if applicable)
-
Name of your legal counsel
-
Your amended and restated articles of incorporation
Industry information
-
Your industry
-
A list of relevant and comparable public companies (Most 409A valuations rely on some form of comparison to publicly traded companies)
Fundraising and options
-
The most probable timing of a liquidity event
-
Your company presentation, business plan, or executive summary
Company financials
-
Historical financial statements
-
Forecasted revenue for the next 12 months, from the valuation date to the next two calendar years
-
Forecasted EBITDA for the next 12 months, from the valuation date to the next two calendar years
-
Cash burn and runway
-
Non-convertible debt amount
Additional details
-
Any materially relevant events since your last 409A valuation (if this is your first-ever 409A, share a complete history of relevant events)
What is a 409A refresh?
After 12 months (or sooner, if there’s a material event), your company will need a 409A refresh—in other words, an updated valuation. Any event that may change the valuation of the company means you need a new 409A.
Download sample 409A valuation report
What is a 409A safe harbor?
When your 409A is handled in a specific way, it’s eligible for “safe harbor” status. Think of it as peace of mind: A safe harbor valuation is one the IRS presumes to be valid unless they can demonstrate that it’s “grossly unreasonable.”
The IRS provides three safe harbor methods for setting the FMV of private company common shares:
-
Independent appraisal presumption
-
Binding formula presumption
-
Illiquid startup presumption
The most common approach to achieving safe harbor status is using the independent appraisal presumption (a qualified, third-party appraiser).
A 409A valuation is presumed reasonable if the stock was valued within 12 months of the applicable option grant date and no material change has occurred between the valuation date and the grant date. If these requirements are met, the burden is on the IRS to prove the valuation is “grossly unreasonable.”
409A penalties
When your 409A valuation isn’t performed using one of the IRS-approved methods, you could fall outside of the 409A safe harbor. The penalties can be substantial for employees and shareholders:
-
All deferred compensation from the current and preceding years becomes taxable immediately
-
Accrued interest on the revised taxable amount
-
An additional tax of 20 percent on all deferred compensation
Most startups aren’t likely to be audited by the IRS. That said, as your company grows and you approach an exit (like a merger, acquisition, or IPO), it’s possible you could face IRS audits. You’ll save time and effort by working with a reputable valuation provider from the beginning.
How do LLCs handle valuations?
Limited liability companies (LLC), differ from corporations in their tax and equity structures, but they still require valuations.
Unlike corporations, LLCs can issue both capital interests ( common and preferred stock, stock options, and warrants), and profits interest units (PIU). PIUs are often assigned a liquidation threshold on their grant date, which is typically equal to the equity value of the company. PIU holders would participate pro rata in future exit proceeds for the amount by which the exit value of the company exceeded the liquidation threshold. The liquidation threshold is often referred to as the distribution or hurdle threshold.
The LLC must keep track of the liquidation threshold for all grantees so that it can accurately track and award profits interests in the future, if applicable.
What is IRC Section 409A?
In response to the 2001 Enron scandal, regulators looked for ways to prevent executives from taking advantage of equity loopholes. The IRS subsequently introduced IRC Section 409A in 2005; a final version went into effect in 2009.
Section 409A contains a framework for private companies to follow when valuing private stock. When the valuation is conducted by an unaffiliated or independent party, it establishes a safe harbor, meaning that it is presumed to be “reasonable” by the IRS—save for a few exceptions.
If a company doesn’t adhere to 409A rules and the equity is priced incorrectly, the IRS can assess penalties. Usually, employees and shareholders end up paying.
Carta provides audit-defensible 409A valuations
Carta is the country’s leading cap table management and 409A valuation provider, trusted with over 15,000 409A valuations each year. We leverage best-in-class software and industry expertise to deliver valuations faster and for less than traditional providers. Carta also offers liquidation threshold valuations for profits interest units alongside its traditional 409A valuation service. Reach out today if you have any questions or need a valuation.